

Ants may be the most successful insects on Earth. They've evolved into sophisticated social insects that fill all kinds of unique niches. From thief ants that rob from other colonies to weaver ants that sew homes in the treetops, ants are a diverse insect group. we will introduce you to some kinds of ants.
Carpenter ants are definitely something to look for in your home. They don't actually eat the wood like termites do, but they do excavate nests and tunnels in structural lumber. Carpenter ants prefer moist wood, so if you've had a leak or flood in your home, be on the lookout for them to move in. Carpenter ants aren't always pests, though. They actually provide an important service in the ecological cycle as decomposers of dead wood. Carpenter ants are omnivores, and will feed on everything from tree sap to dead insects. They're quite large, with the major workers measuring a full 1/2 inch in length.

Tiny Pharaoh ants are pervasive, hard to control pests that invade houses, grocery stores, and hospitals. Pharaoh ants are native to Africa, but now inhabit dwellings worldwide. They're a serious concern when they infest hospitals, as these pests carry a dozen infectious pathogens. Pharaoh ants feed on everything from soda to shoe polish, so just about anything can attract them. The name Pharaoh ant was given to this species because they were once believed to be one of the plagues of ancient Egypt. They're also known as sugar ants or piss ants.

Harvester ants inhabit deserts and prairies, where they harvest plant seeds for food. They store the seeds in underground nests. If the seeds get wet, the harvester ant workers will carry the food stores above ground to dry them and keep them from germinating. Harvester ants build mounds in grassy areas, and defoliate the area around their central nest site. Like fire ants, harvester ants will defend their nest by inflicting painful bites and venomous stings. One harvester ant species, Pogonomyrmex Maricopa, possesses the most toxic insect venom known.

The common bed bug (Cimex lectularius) has long been a pest – feeding on blood, causing itchy bites and generally irritating their human hosts.) All health departments consider bed bugs a public health pest. However, unlike most public health pests, bed bugs are not known to transmit or spread disease.
They can, however, cause other public health issues, so it’s important to pay close attention to preventing and controlling bed bugs.
Experts believe the recent increase in bed bug in the United States may be due to more travel, lack of knowledge about preventing infestations, increased resistance of bed bugs to pesticides, and ineffective pest control practices.
The good news is that there are ways to control bed bugs. Getting good, solid information is the first step in both prevention and control. While there is no chemical quick fix, there are effective strategies to control bed bugs involving both non-chemical and chemical methods.
Bed bugs can be hard to find and identify, given their small size and their habit of staying hidden. It helps to know what they look like, since the various life stages have different forms.

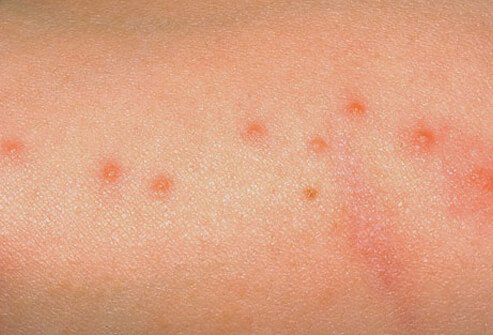
Cockroaches are among the most common insect pests in homes, schools, and businesses. They like to eat many of the same foods we do and are especially troublesome wherever food is prepared or served. They also may transfer disease-causing organisms.
Fortunately, cockroaches can be controlled with a little knowledge about their biology and behavior, attention to sanitation, and effective use of commercially available insecticides.
American cockroaches, also known as waterbugs or palmetto bugs, are more common in commercial buildings and are one of the most common cockroaches in sewer systems. The largest cockroach in Texas, it can grow 1½ to 2 inches long. Both the adult male and the female can fly.
Adults are reddish brown (Fig. 1a), with tan to light- yellow bands outlining the pronotum. Young nymphs are grayish brown, but after the first few molts, they become more reddish brown (Fig. 1b). American cockroaches are long lived, reaching adulthood and sexual maturity in an average of 600 days. As adults, they usually live 1 to 2 years.

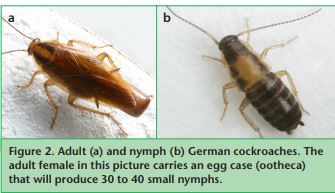
German cockroach adults are ½ to ⅝ inch long and are light brown with two dark stripes on the pronotum (Fig. 2a). Both males and females have wings extending to the end of their abdomens but they do not fly. Nymphs have wing pads and two dark stripes extending down the entire thorax and abdomen (Fig. 2b).
German cockroaches are the most prolific of indoor cockroaches and can produce a generation in about 100 days. They are one of the most widespread insect pests to public health in urban homes, apartments, and restaurants. They transport germs and are associated with allergies and asthma.
German cockroaches do not live outdoors in Texas. The Asian (Blattella asahinai) and field (Blattella vaga) cockroaches look very similar to German cockroaches and may be found outdoors in some areas of the state.
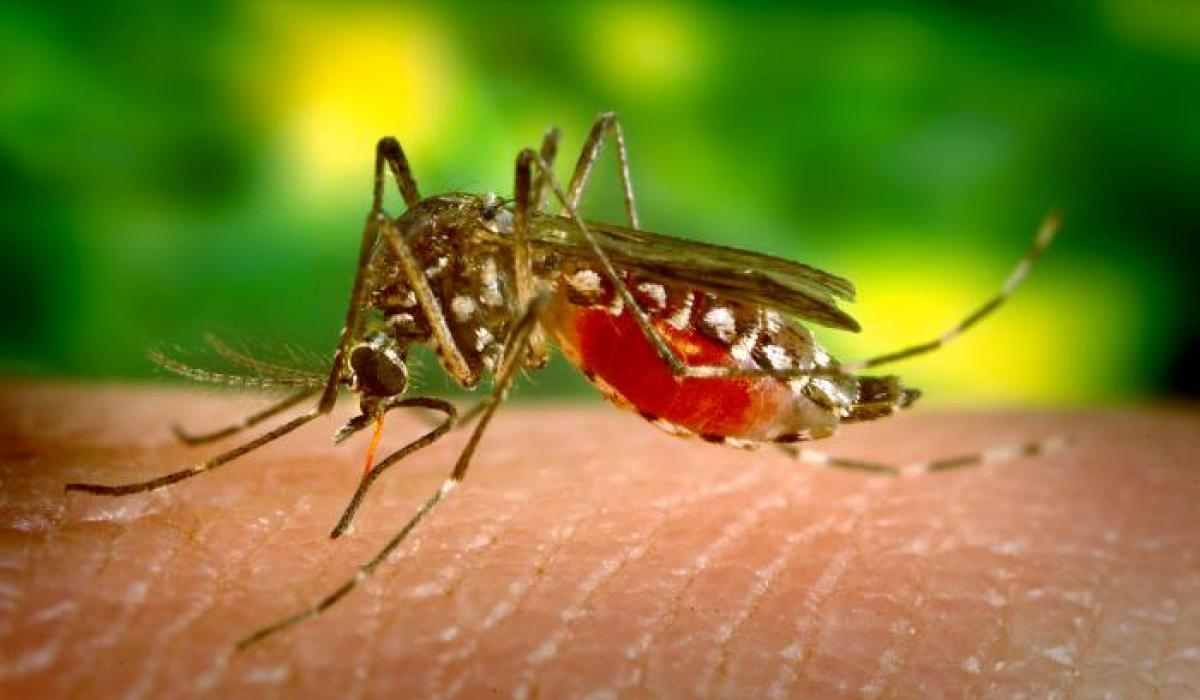
Almost everyone has had the unpleasant experience of being bitten by a mosquito. Mosquito bites can cause skin irritation through an allergic reaction to the mosquito's saliva - this is what causes the red bump and itching. But a more serious consequence of some mosquito bites may be transmission of serious diseases and viruses such as malaria, dengue virus, Zika and West Nile virus, which can lead to disabling and potentially deadly effects (such as encephalitis, meningitis and microcephaly)
There are three important mosquito genera. Anopheles, the only known carrier of malaria, also transmits filariasis and encephalitis. Anopheles mosquitoes are easily recognized in their resting position, in which the proboscis, head, and body are held on a straight line to each other but at an angle to the surface. The spotted colouring on the wings results from coloured scales. Egg laying usually occurs in water containing heavy vegetation. The female deposits her eggs singly on the water surface. Anopheles larvae lie parallel to the water surface and breathe through posterior spiracular plates on the abdomen instead of through a tube, as do most other mosquito larvae. The life cycle is from 18 days to several weeks.
The genus Culex is a carrier of viral encephalitis and, in tropical and subtropical climates, of filariasis. It holds its body parallel to the resting surface and its proboscis is bent downward relative to the surface. The wings, with scales on the veins and the margin, are uniform in colour. The tip of the female’s abdomen is blunt and has retracted cerci (sensory appendages). Egg laying may occur on almost any body of fresh water, including standing polluted water. The eggs, which float on the water, are joined in masses of 100 or more. The long and slender Culex larvae have breathing tubes that contain hair tufts. They hang head downward at an angle of 45° from the water surface. The life cycle, usually 10 to 14 days, may be longer in cold weather.

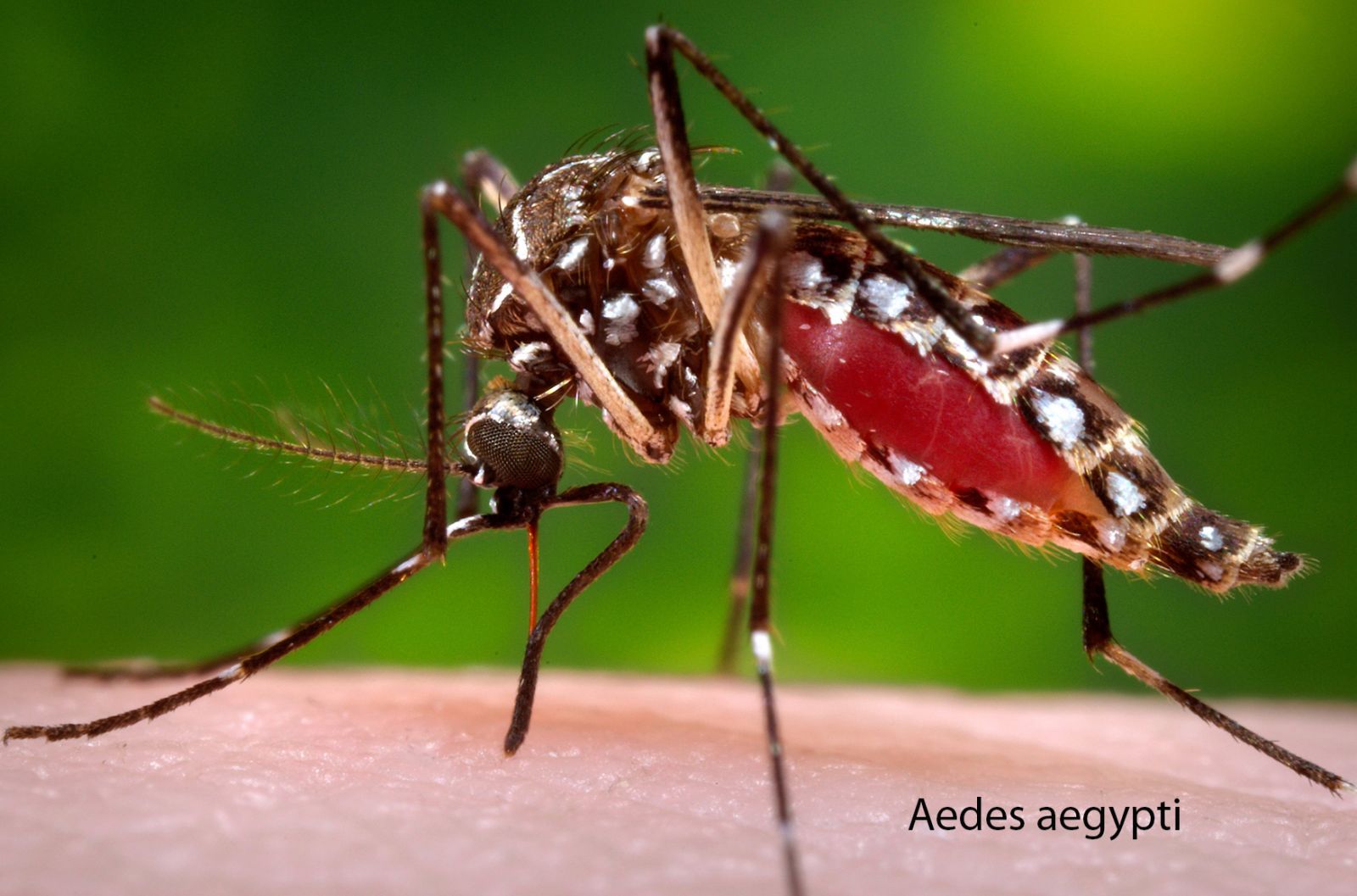
The genus Aedes carries the pathogens that cause yellow fever, dengue, Zika fever, and encephalitis. Like Culex, it holds its body parallel to the surface with the proboscis bent down. The wings are uniformly coloured. Aedes may be distinguished from Culex by its silver thorax with white markings and posterior spiracular bristles. The tip of the female’s abdomen is pointed and has protruding cerci. Aedes usually lays eggs in floodwater, rain pools, or salt marshes. The eggs are capable of withstanding long periods of dryness. The short, stout larvae have a breathing tube containing a pair of tufts, and the larvae hang head down at a 45° angle from the water surface. The life cycle may be as short as 10 days or, in cool weather, as long as several months. A. aegypti, the important carrier of the virus responsible for yellow fever, has white bands on its legs and spots on its abdomen and thorax. This domestic species breeds in almost any kind of container, from flower pots to discarded car-tire casings. They are prolific breeders, strong fliers, and irritants to animals, including humans.

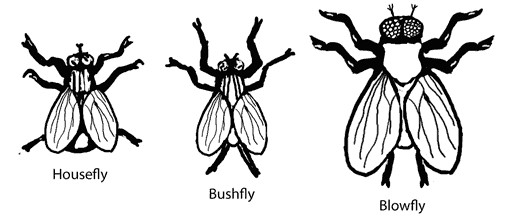
There are many different kinds of flies. Three common types are shown below:
Adult flies lay their eggs in moist organic material, for example, food scraps, animal faeces (droppings), grass clippings or dead animals. After a few hours the eggs turn into larvae, called maggots.
The maggots feed on the organic material and grow quickly. After four or five days the maggots move to dry soil and burrow down into it and turn into pupae. A special hard protective covering called a pupal case encloses each of the pupae while they continue to develop. Pupae are brown to black in colour and can sometimes be mistaken for mice droppings.
After four or five days, pupae turn into adult flies. They break out of the pupal case, burrow up through the soil to the surface and fly away. Flies are able to travel many kilometers from their breeding place. However, if there are lots of flies around, it usually means there is a good breeding place nearby.

When flies land on things like food scraps, manure, faeces or dead animals they pick up disease-carrying germs and germs. The germs are carried on their hairy bodies and legs and in their stomachs.
When the flies land on things like food, cups, knives and plates, the germs can be passed on to these articles. If people then eat the food or use these articles when eating food, they will get the germs into their bodies and may become sick.
Flies feed by putting a special substance from its stomach onto the food through its long, hollow, tube-shaped mouth. This special type of mouth is called a proboscis. The special substance which comes from the fly's stomach makes the food liquid and the fly then sucks this up through its proboscis.
Germs from the fly’s legs and body, and from the liquid that comes from its stomach, get onto the food while it is eating. Some of these germs will be left behind on the food after the fly has gone.
This is a list of the diseases caused by germs and parasites which come from flies.
Diseases in Indigenous communities caused by germs carried by flies:
Bacterial diseases:
Rodents can spread dangerous diseases and can cause major property damage, so it's important for homeowners to familiarize themselves with the types of rodents that invade homes this time of year. Here is a guide to help you identify common mice and rat species.

If you suspect an infestation, contact a licensed pest professional. Rodents are known to reproduce quickly, and what may seem like a small problem can turn into a big issue overnight.
The common house spider gets its name from the fact that it is usually the spider most often encountered indoors. It is a nuisance pest, probably more because of its webs than the spider itself. The house spider is found worldwide and is common throughout the United States and Canada. Read on to learn more information, including advice on house spider control.
Female house spiders lay about 250 eggs in a silken sac that is brownish in color and round in shape. There may be more than one sac in the web at a time. A female house spider may produce up to 17 sacs, containing a total of more than 3,760 eggs, in her lifetime. The eggs hatch in about 7-10 days. Adults may live for a year or more.

To prevent common house spiders from entering the home, seal cracks around the outside of the house using a silicone-based caulk. Also, screen windows and doors. If you find a house spider inside, you can get rid of it by using a vacuum to remove adults, egg sacs and webs. If a broom is used, adult house spiders can usually escape. Contact a licensed pest control professional if you suspect a spider infestation in the home.